We visit a lot of websites every day. Sometimes we need to collect some pieces of information. How can we do this? The only solution is to copy-paste or saving the page as a PDF? Let’s take an example; Rocomari is a Bangladeshi online marketplace for ordering books. They sell books with discounts in different categories. So you want to buy a book with a 40% discount. You want notifications when that book will sell at a 40% discount. Here, web scraper may help you in a better way instead of looking through the website each day manually.
In this article, I’m going to share some basic knowledge on web scraping and python Beautiful Soup package to collect corona related Bangla news from Bangladeshi websites.
 web scraper; source: codecanyon
web scraper; source: codecanyon
Web Scraping
According to Wikipedia,** Web scraping, **web harvesting, or web data extraction is data scraping used for extracting data from websites. Web scraping is the process of automatically mining data or collecting information from the World Wide Web.
If you’ve ever copy and pasted information from a website, you’ve performed the same function as any web scraper, only on a manual scale.
Why do we need Web Scraping?
As we know that web scraping is used to extract data from websites. These raw data are used for many fields including Market Research, user’s email collecting, news, and content monitoring, research and development, price comparing, etc.
Is it legal?
The legality of web scraping varies across the world. In general, web scraping may be against the terms of use of some websites. [Wikipedia]
If scraping violates any terms of service of a website then it must be illegal. Many popular websites don’t allow web scraping for privacy concerns.
How do Web Scrapers Work?
Web Scrapers can be an automated bot to run automatically for collecting data from a website and storing those collected data with some formats.
](https://cdn-images-1.medium.com/max/2000/1*VuK7xbtcG2ArT3Fxb47P_Q.png) Web Scraping; source: link
Web Scraping; source: link
First, the web scraper will be given one or more URLs to load before scraping. The scraper then loads the entire HTML document for the page. Then the scraper will parse the specific HTML document from the entire page.
You can select the specific data that you want from the page. For example, in the above example, You just want to know the discount on a single book.
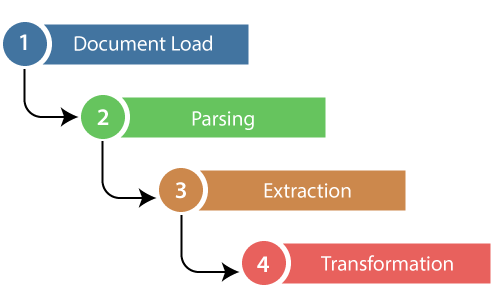 web scraping steps; source: javatpoint
web scraping steps; source: javatpoint
Then, the web scraper will extract the information from the page and lastly, that collected information will be transferred with a specific format.
Most web scrapers will output data to a CSV or Excel spreadsheet, while more advanced scrapers will support other formats such as JSON which can be used for an API.
Why Python for Web Scraping?
Python is the most popular language for web scrapping comparing other popular programming languages. It has lots of libraries, and we can do programming in less coding.
Getting Started with Web Scraping
There are many packages for web scraping with python. I’m using Beautiful Soup (bs4) package here to scrape ‘Corona related Bangla news’.
Let’s first install the required package, from your virtual environment run the following command:
pip install bs4

let’s create a scraper who will take an URL as an argument and will return the HTML document.
import requests
from requests.exceptions import HTTPError
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
def scrape_url(url, headers=None):
try:
page = requests.get(url, headers)
page.raise_for_status()
except HTTPError as e:
print(e)
except Exception as err:
print(err)
else:
soup = BeautifulSoup(page.content, 'html.parser')
soup = BeautifulSoup(soup.prettify(), 'html.parser')
return soup
return BeautifulSoup("", 'html.parser')
if the URL is not valid or can’t respond then it will return an empty document. in the following code, headers work as a browser agent. to get your browser agent: type in google search “my user agent”

copy it and pass it into the function as a variable. if you want you can skip browser agent. run the following command to get the document.
soup = scrape_url("https://somoynews.tv", my_user_agent)
print(type(soup))
In return, you will get an object of the bs4 class type.
Since we want only corona related news posts, see we need to find only the links. to find all links:
all_links = soup.find_all('a')
all_links also, bs4 object contains only ‘a’ link attribute. Now, we need to filter and remove all the non-corona related Bangla news.
So, let’s make a statement that those link titles don’t contain any words of the corona that are not related to it.
training_samples = ['করোনা', 'কোভিড-১৯', 'উহান-ভাইরাস']
If any news title contains any words of traning_samples that means that news are corona related. following code to match corona related news:
soup = scrape_url("https://somoynews.tv")
all_links = soup.find_all('a')
training_samples = ['করোনা', 'কোভিড-১৯', 'উহান-ভাইরাস']
for link in all_links:
title_words = link.get_text().strip().split()
if set(training_samples).intersection(set(title_words)):
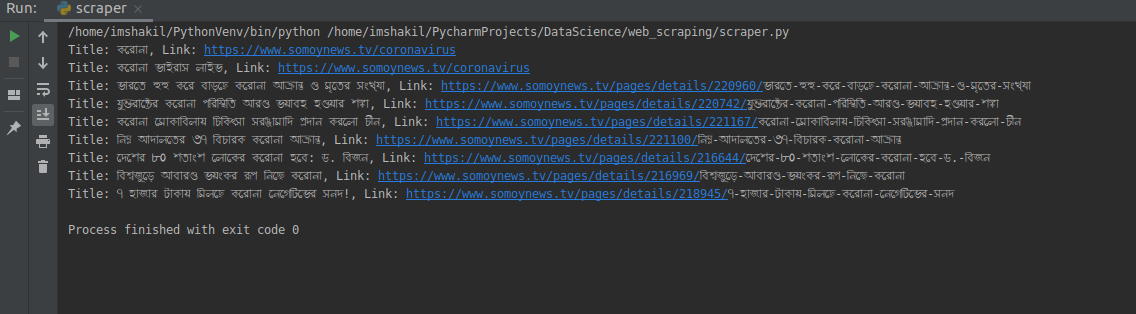
print("Title: {}, Link: {}".format(link.get_text().strip(), link.get('href')))
following result:
Completed code:
We can add multiple website, to get more news. also if we use meta data extraction then more news can be found. I have uploaded a complete code in github.
Github link of this sample project: https://github.com/imShakil/DataScience/tree/master/web_scraping
That’s all for this article. If you want to know more about Beautiful Soup; Please, read from the official documentation: https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/