
An application is maintained over and overtime to fix its bugs, adding new features, changing its user interface, etc. If we look at apple or google play store, we see Facebook, Instagram, Whatsapp, etc, these applications are updated once or twice every month where each update has a version name like v2.1, v2.2. Managing versions of software with ease and flexibility Version Control plays a major role in the software industry.
Version Control System
Version control is a system that records changes to a file or set of files over time so that you can recall specific versions later. (Git)
Let’s say you are developing an android application to complete your final year project. At a specific point, you may realize that some bug has been found in your code and you want to roll back your previous code. Without keeping record each change that won’t be possible to roll back. That’s how a version control system may help you.
Version control systems allow you to make periodic, manual “commits” to your project’s “repository” to save code as you want. Every time you make a commit to the project, the version control system records these commits as a version of your project. If you ever want to go back to an exact version of your project at a specific time, you can simply get back by recalling the specific commit. Git, Mercurial, Apache Subversion, CVS, etc are a few examples of version control systems. Among these Git is the most popular version control system used by most software industries in the entire world. Facebook uses Mercurial as its version control system as a large software company in the world.
Git
What’s Git?
Git is a distributed version control system. Git installs locally on computers. It’s a free and open-source command-line tool.
Git Installation
According to your device and operating system, you can setup Git from their website.
If you are a Linux user then use this command to install it on your computer:
sudo apt install git-all
GitHub
What is GitHub?
GitHub is designed as a git repository hosting service. You can share your projects with others to work together as a team. It’s the largest online platform used by the 37 million users around the world.
GitHub has free and premium plans varying their services.

GitHub also likes a GUI for the git command-line tool. It makes more easy to learn how Git works. Simply create an account from their website to start using their services.
Build software better, together
_GitHub brings together the world’s largest community of developers to discover, share, and build better software. From…_github.com
Major Concepts on Git and GitHub
Before getting started with Git and GitHub, let’s know the major concepts of Git and GitHub for better understand.
Repository
The repository is the most important component of the version control system. A repository can be viewed as a folder or project with a set of files and subfolders.
git init
This command is used to create a folder as a git repository. After performing this command, a .git folder is created where each change of file is recorded. Thie metadata is everything of a git repository. This folder doesn’t show in your GitHub repository rather than it can be found on your local machine when you clone a git repository.
Workspace
A workspace is something that you don’t want to share as open-source or somewhere like GitHub. These things only work when you want to share your project with an online platform like GitHub. You may find a file like .gitignore that ignores the information that you don’t want to share in Github or another online hosting platform.
Tracked and Untracked
Each file in your working directory can be in one of two states: tracked or untracked. Tracked files are files that were in the last snapshot; they can be unmodified, modified, or staged. In short, tracked files are files that Git knows about. To track files:
git add file1 file2...
git add --all
git add .
1st command can be used to add specific files in the track whereas 2nd and 3rd command can be used to add all files in the track.
Untracked files are everything else — any files in your working directory that were not in your last snapshot and are not in your staging area. When you first clone a repository, all of your files will be tracked and unmodified because Git just checked them out and you haven’t edited anything.
As you edit files, Git sees them as modified, because you’ve changed them since your last commit. As you work, you selectively stage these modified files and then commit all those staged changes, and the cycle repeats.

To check git status use below command line:
git status
Commits
Commits are a major part of the version control system. Commits keep track of file changes. You can manually add commits from GitHub or using Git command. To commit from Git command line:
git commit -m “description of your commit”
There are two types of commits: stage and unstage . When you add or edit a file in your repository git will track these changes as unstaged since they are yet to verify. When you commit these changes will be marked as staged.
Branches
Branching means you diverge from the main line of development and continue to do work without messing with that main line.

The ‘master’ branch is the main branch of the project. This ‘master’ branch merge files that are pushed from other branches. It will be more clear when you are used to be with GitHub.
Push, Pull and Pull Request

From the above picture, you may think about how pull & push works in a git repository.
When you push changes to a repository, you’re specifying what changes will be made to a specific branch in the version control system.
When changes have been made on GitHub, for example, but differ from that which exist locally on an individual’s machine, that individual can initiate a pull from that repository to get the appropriate updates to his version of the software locally.
A pull request exists when permission must be granted in order for a pull of changes to be brought into a specific part of the version control system. Suppose, you have updated a file in a public repository and then you want to share with the master branch of that repository then you can send a pull request to the master branch.
Remotes
Remote repositories are versions of your project that are hosted on the Internet or network somewhere. You can have several of them, each of which generally is either read-only or read/write for you. Collaborating with others involves managing these remote repositories and pushing and pulling data to and from them when you need to share work. Managing remote repositories includes knowing how to add remote repositories, remove remotes that are no longer valid, manage various remote branches, and define them as being tracked or not, and more. (Git)
To check remotes in your git repository use this command:
git remote
or to see with repository URL:
git remote -v
To add remote:
git remote add “remote name” “remote url”
To remove remote:
git remote remove "remote name"
Merging
Merging in git repository means combining branches with the master branch in the version control system.
So now, we know some basic commands and functionality of git and Github. In the last part of this article, I’m going through an example to show you how to create a repo in Github, cloning it into our local machine using Git command, adding some changes into that repo, commit those changes, and pushing changes up to GitHub, then creating a pull request and finally merging it to master branch.
Getting Started with Git and GitHub
Let’s start with a repository to understand Git and Github in a better way.
-
Go to the Github website and log in using your Github account.
-
Navigate to the top right corner and click into the ‘+’ icon then chose
new repositoryto create a repo.

- Chose a repository name and set a description, choose public so that anyone can see it in your profile, choose to initiate with a readme.md file then create a repository

If you want to skip the above steps then you can just start from step-4 to clone my repository and contributing as a team member.
- Let’s clone the created repository into our local machine(computer). before cloning it, let’s check that git is working or not on our computer. to check enter following command:
git --versionyou will see an output with a version: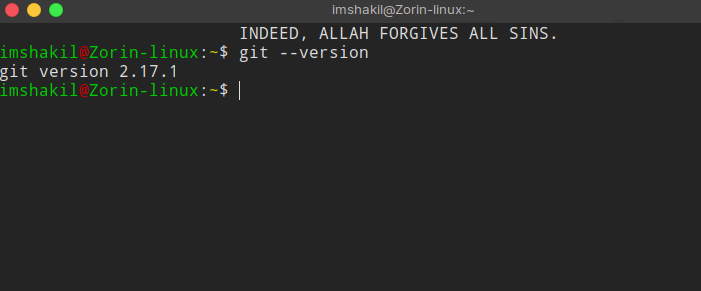
okay, git is fine. let’s clone the repository. choose a directory where you want to clone it. Then perform the following command:
git clone [https://github.com/imShakil/test.git](https://github.com/imShakil/test.git)
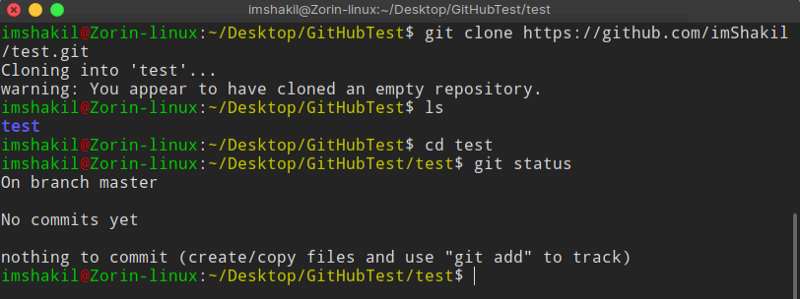
Now you have a version of your repository into your local machine. You can perform some git command to see what happens like:
git status
git remote
git branch
- Now let’s create a branch named ‘demo’:
To create a branch:
git checkout -b “branch name”
To see list of branch:
git branch
To delete a branch:
git checkout -d "branch name"
To switch from the current branch to another branch:
git checkout "branch name"

- Adding a python hello world in this repo.
git add hello.py

- Let’s commit to recording these changes:
git commit -m “python hello world added”

- Okay, now we are going to push these changes to the “demo” branch in the Github repository from our local machine.
First, set upstream of branch “demo” to the remote “origin”
git --set-upstream origin demo
Then push it
git push
After successfully pushed it to Github, you will see the difference between master and demo branches as below in Github:
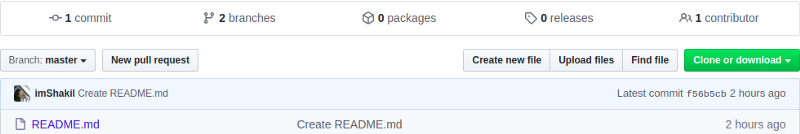
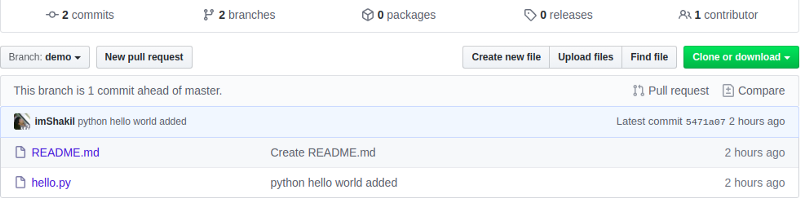
also, you can check the differences between any two branches locally on your computer.
git diff master demo
You will see the differences:

- Let’s make a pull request from “demo” branch to the “master” branch.

When you switch demo branch in Github you may see something “This branch is 1 commit ahead of master”. Now click on “New pull request” to create a pull request.
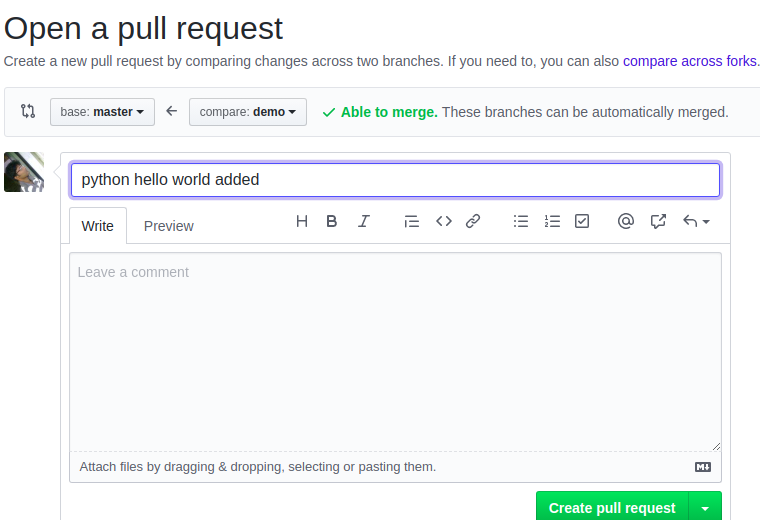
You can say something relevant with the pull request then create a pull request.
- After successfully sending a pull request, the master branch can merge the pull request, even he can modify the changes.

Just click on the “merge pull request” to merge it with the “master” branch.
So, The “master” branch is updated now in Github but not in your local machine (Computer).
- To update the master branch in your computer locally you need to run a pull command.
First, make sure you are on the master branch:
git checkout master
Now, run a pull command:
git pull origin master

I hope you understand Version Control, how Git and Github works, and how to use those tools to control software versions.
N.B: In this article, I have used a personal repository to create multiple branches, making pull requests. But, If you want to contribute to a public repository then, you must have to fork it in your Github profile then you can do all the things as described in this post.
References:
[2]: https://help.github.com/en/github